Headaches are one of the most common medical complaints experienced by people of all ages. They can range from minor discomfort to debilitating pain, impacting an individual's quality of life. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of headaches, including their types, epidemiology, treatments, symptoms, causes, and prevention strategies.
Epidemiology
Headaches are a widespread health concern, with varying prevalence depending on the type. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), almost half of the adult population worldwide experiences headaches at least once a year. Migraines, in particular, affect about 10% of the global population, and tension headaches are even more prevalent. Although headaches can affect anyone, certain factors, such as gender, age, genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, can influence the risk of experiencing them.
Types of Headaches
Headaches can be classified into primary and secondary headaches.
1. Primary Headaches: These are stand-alone conditions and not caused by an underlying medical condition. The most common types of primary headaches are:
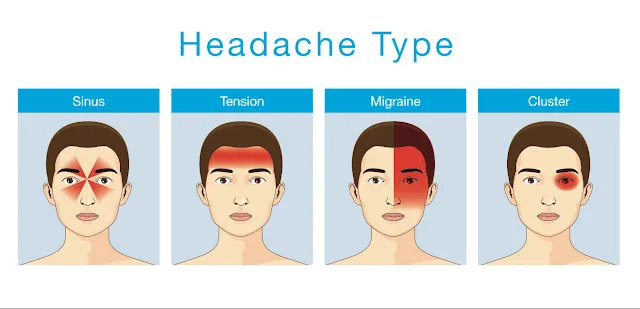
a) Tension headaches: These headaches are characterized by a constant dull pain or pressure on both sides of the head, often associated with muscle tension or stress.
b) Migraine headaches: Migraines are intense, throbbing headaches that can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances.
c) Cluster headaches: Cluster headaches are severe and occur in cyclical patterns, often characterized by excruciating pain on one side of the head, accompanied by nasal congestion, tearing, and restlessness.
2. Secondary Headaches: These headaches are symptoms of an underlying medical condition or injury. Some common causes include:
a) Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses can lead to headaches, often felt as pressure around the eyes, cheeks, and forehead.
b) Head injury: Concussions, trauma, or other head injuries can cause headaches.
c) Medication overuse headache: Overuse or long-term use of certain pain medications can lead to rebound headaches.
d) Infections: Headaches can occur as a result of infections such as meningitis or encephalitis.
e) Hormonal changes: Some women experience headaches associated with hormonal changes during menstruation or menopause.
Symptoms
Headache symptoms can vary depending on the type and underlying cause. Common symptoms may include:
- Dull, aching pain or intense throbbing sensation
- Sensitivity to light, sound, or certain smells
- Nausea or vomiting
- Visual disturbances or aura
- Stiff neck or shoulder muscles
- Nasal congestion or runny nose
- Changes in mood or irritability
Causes
Headaches can have various causes, including but not limited to:
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may have a familial tendency to experience certain types of headaches, such as migraines.
- Environmental triggers: Certain factors like strong smells, loud noises, bright lights, or weather changes can trigger headaches in susceptible individuals.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in estrogen levels during the menstrual cycle or hormonal imbalances can contribute to migraines in some women.
- Stress and tension: Emotional stress, anxiety, or tension can cause or exacerbate headaches, especially tension headaches.
- Physical factors: Poor posture, neck or shoulder strain, or excessive physical exertion can lead to headaches.
- Certain foods and drinks: Alcohol, caffeine, processed foods containing additives, and specific food items can act as triggers for migraines in susceptible individuals.
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent all headaches, certain strategies can help reduce the frequency and severity of episodes. These include:
- Identifying triggers: Keeping a headache diary to record potential triggers (such as food, stressors, or environmental factors) can help individuals identify and avoid triggers in the future.
- Stress management: Engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help manage stress and reduce the likelihood of tension headaches.
- Adequate sleep: Establishing and maintaining regular sleep patterns can promote overall well-being and prevent sleep deprivation-induced headaches.
- Healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption can contribute to headache prevention.
- Seeking medical care: If headaches become frequent, severe, or significantly impact daily life, consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate management is essential.
Treatments
Headache treatment aims to relieve pain and improve a person's overall well-being. Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the headache, as well as individual factors. Common approaches include:
1. Medications
a) Over-the-counter pain relievers: Non-prescription drugs like acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or aspirin can often alleviate mild to moderate headaches.
b) Triptans: These medications are specifically designed for the treatment of migraines and work by reducing inflammation and constricting blood vessels in the brain.
c) Preventive medications: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, antidepressants, or anti-seizure drugs, may be prescribed to help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches in chronic cases.
2. Lifestyle modifications
a) Stress reduction techniques: Practices like relaxation exercises, meditation, and yoga can help manage stress and decrease tension headaches.
b) Regular sleep patterns: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, ensuring sufficient rest, and creating a relaxing sleep environment can aid in preventing headaches.
c) Dietary changes: Identifying and avoiding trigger foods (such as processed meats, aged cheeses, or caffeine) can help manage migraines.
d) Hydration: Staying adequately hydrated can prevent headaches caused by dehydration.
In conclusion, headaches are a common health concern experienced by people worldwide. Understandably, their impact can be significant, affecting daily activities, productivity, and overall well-being. By familiarizing ourselves with the different types of headaches, their causes, available treatments, and prevention strategies, we can take proactive steps to manage headaches effectively. In cases where headaches become debilitating or persist despite self-care measures, seeking professional medical advice is crucial to ensure proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.


Post a Comment
Full Name :
Adress:
Contact :
Comment: